Lentinus squarrosulus Mont. Selectively Stimulates Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus growth and inhibits pathogenic bacteria: A promising prebiotic potential
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/gjpb.2025.2.7Keywords:
Lentinus squarrosulus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus pentosus, prebioticsAbstract
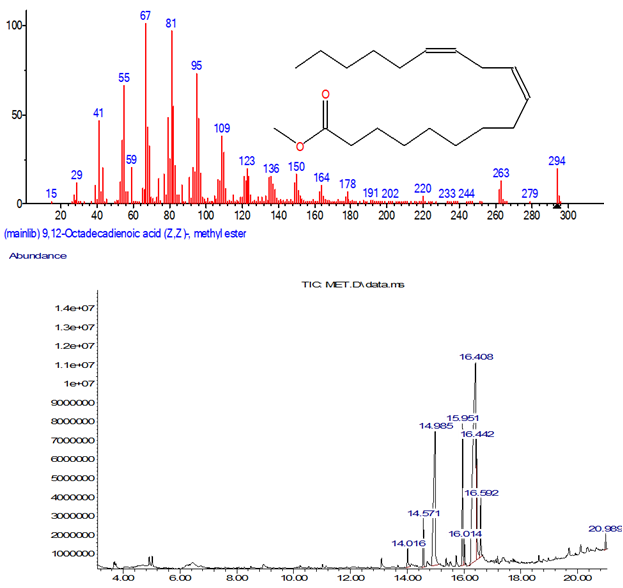
Prebiotics are agents that can selectively stimulate the growth of beneficial microorganisms (probiotics). Mushrooms have been reported as a significant source of prebiotics. This study investigates the prebiotic potential of Lentinus squarrosulus Mont. Fruiting bodies of L. squarrosulus were lyophilized, pulverized, and extracted with chloroform/methanol (1:1) and distilled water. The percentage growth stimulation effect of the mushroom extracts on Lactobacillus plantarum AO11 and Lactobacillus pentosus A4c, as well as their activity against pathogenic bacteria, including enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EPEC 034A, Salmonella typhi ATCC 14028, and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, was determined using standard methods. Inulin and ciprofloxacin served as controls.Chemical composition of the mushroom extract was identified using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Culture media supplemented with 20 mg/ml of the aqueous extract of L. squarrosulus produced a 74% growth stimulation of Lactobacillus plantarum, which is comparable to that of inulin (75%), a commercial prebiotic. The zone of inhibition of the supernatant of Lactobacillus species cultured in media supplemented with mushroom extracts, inulin, or ciprofloxacin against E. coli, S. typhi, and S. aureus ranged from 10 to 23.5 mm. The supernatant of Lactobacillus plantarum AO11 and Lactobacillus pentosus A4c cultured in media supplemented with the CME (26-57%), inulin (40-54%), or ciprofloxacin (54-59%) showed greater activity against pathogenic organisms than the supernatant of extract-free culture media. Notable compounds in the aqueous extract include 9,12- octadecadienoic acid (Z, Z methyl ester), n-hexadecanoic acid, and oleic acid. Lentinus squarrosulus stimulates Lactobacillus plantarum AO11 and Lactobacillus pentosus A4c. growth and inhibits pathogenic organisms. Its usefulness in promoting gut health could be further explored.
Metrics
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oyindamola O. Abiodun, Oluwayimika F. Olumide, Olumuyiwa S. Alabi, Abiola O. Obisesan, Bolaji B. Oluremi, Ayomide, A. Ajibewa, Tunde F. Ogunrotimi, Adedunke O Oshinloye

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







