Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is essential for the protective effect of Fat soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, and K) on colorectal cancer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/gjpb.2025.2.5Abstract
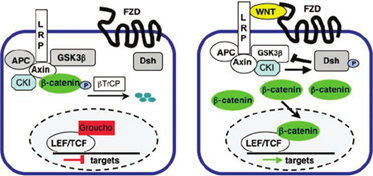
An essential regulatory pathway involved in many biological processes, such as embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and cancer progression, is the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. One of the main characteristics of Colorectal Cancer (CRC) is the dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which plays a significant role in tumor development, invasion, and metastasis. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene mutations account for 80–90% of sporadic cases of CRC. Typically, APC mutations occur early in the development of CRC. APC normally suppresses tumors by encouraging β-catenin degradation. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as A, D, E, and K, are essential for many physiological functions. They may also interact with signaling pathways like the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The involvement of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the protective effect of Fatsoluble vitamins against CRC is the main topic of this review. Moreover, a comprehensive understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms of fat-soluble vitamins-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulation is required to target therapeutic targets for CRC prevention and treatment effectively.
Metrics
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hossna M. Ismail, Ehab S. Shatat, Abdel-Aziz S. Shatat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







